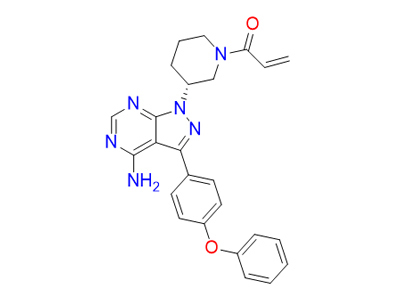
IUPAC name
1-[(3R)-3-[4-amino-3-(4-phenoxyphenyl)pyrazolo[3,4-d]pyrimidin-1-yl]piperidin-1-yl]prop-2-en-1-one

1-[(3R)-3-[4-amino-3-(4-phenoxyphenyl)pyrazolo[3,4-d]pyrimidin-1-yl]piperidin-1-yl]prop-2-en-1-one
936563-96-1
440.5 g·mol−1
C25H24N6O2
Granule: Available
Ready to press o
Ready to fill þ
The B cell receptor (BCR) pathway regulates lots of cellular processes including, proliferation, differentiation, and apoptosis which are essential for the functioning and survival of both normal and malignant B cells. In B cell malignancies, such as CLL; aberrant BCR signaling plays a critical role in the pathogenesis of disease. The BCR pathway is responsible for the phosphorylation of numerous protein tyrosine kinases (PTKs), including Lyn, SYK, and Bruton’s tyrosine kinase (BTK). These PTKs showed constitutively and over-expressed activity in CLL, which leads to uncontrolled proliferation and survival of malignant B cells, so, there has been rapid clinical development of inhibitors targeting these PTKs. Among the many PTKs involved in BCR signaling, BTK, a tyrosine kinase member of the Tec kinase family, is a distinctive therapeutic target. Upon BCR activation, BTK becomes activated by other PTKs, such as Lyn and SYK, resulting in activation of downstream transcription factors necessary for B cell proliferation and differentiation.
Ibrutinib is a highly potent, selective, and irreversible small-molecule inhibitor of BTK. It forms a covalent bond with a cysteine residue (CYS-481) at the active site of BTK, leading to inhibition of BTK enzymatic activity. It can also abrogate the full activation of BTK by inhibiting its auto phosphorylation at Tyr-223. This inhibition prevents downstream activation of the BCR pathway and subsequently blocks cell growth, proliferation, and survival of malignant B cells.